Uttam AESA Radar – All You Need To Know
Uttam AESA Radar is an Active Electronically Scanned Array Radar developed by the Electronics and Radar Development Establishment of DRDO. The main aim of Uttam AESA Radar is to be installed in LCA Tejas Mk1A, Tejas Mk2, AMCA, and TEDBF fighter jets. AESA stands for Active Electronically Scanned Array Radar. The Modern Aircraft and Naval Vessels are equipped with the AESA Radar.
First, let’s understand how the Radar works. Radar stands for Radio Detection and Ranging. The transmitter sends a pulse signal in the air, the pulse signal strikes the object and is then reflected back. The time difference between the transmission and reflection is calculated to locate the object.
AESA radar is computer controlled array antenna. In AESA, each antenna element is connected to TRM (Transmitter/Receiver Module) independently. This complicated module of AESA allows the radar to emit multiple radio waves at multiple frequencies simultaneously. The beam of radio waves can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the antenna.
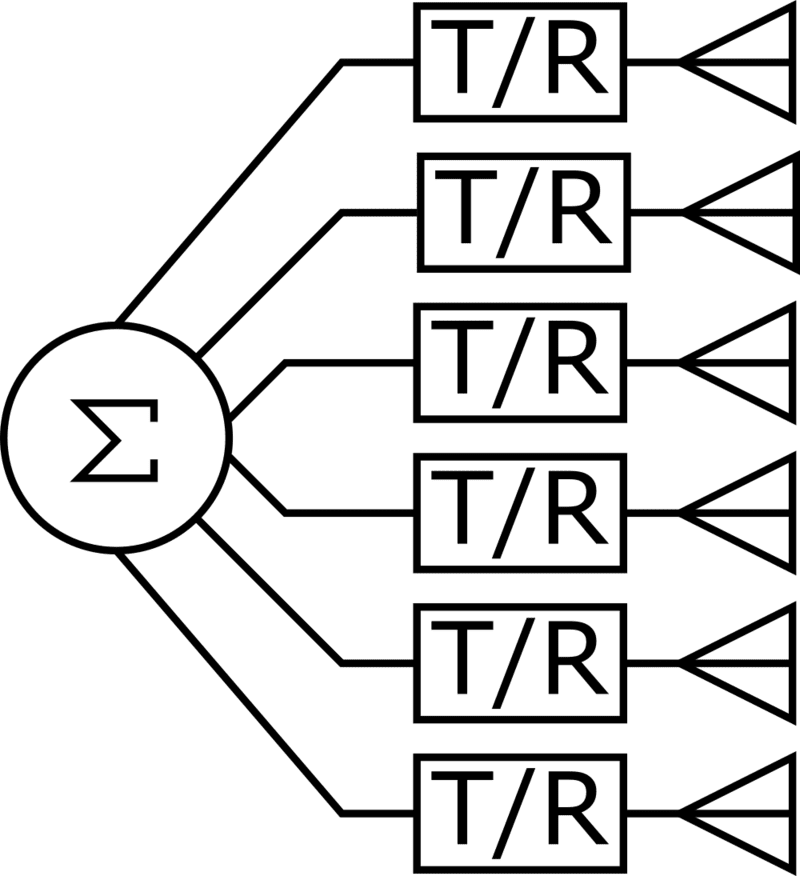
But in PESA Radar (Passive Electronically Scanned Array Radar), all the elements of antennas are connected to a single Transmitter/Receiver through phase shifters
The few advantages of AESA Radar are:
- Low probability to intercept
- High Jamming Resistance
Uttam AESA Radar
Uttam is a solid-state gallium arsenide-based AESA Radar developed by LRDE DRDO. The Radar can track up to 50 targets and engage 4 targets simultaneously.
Some of the key features of Uttam Radar are:
- Extended detection range
- Multi-target tracking
- High ECM (Electronic Counter Measures) immunity
- High-Resolution Imaging
- Weather tracking
- Doppler Beam Sharpening
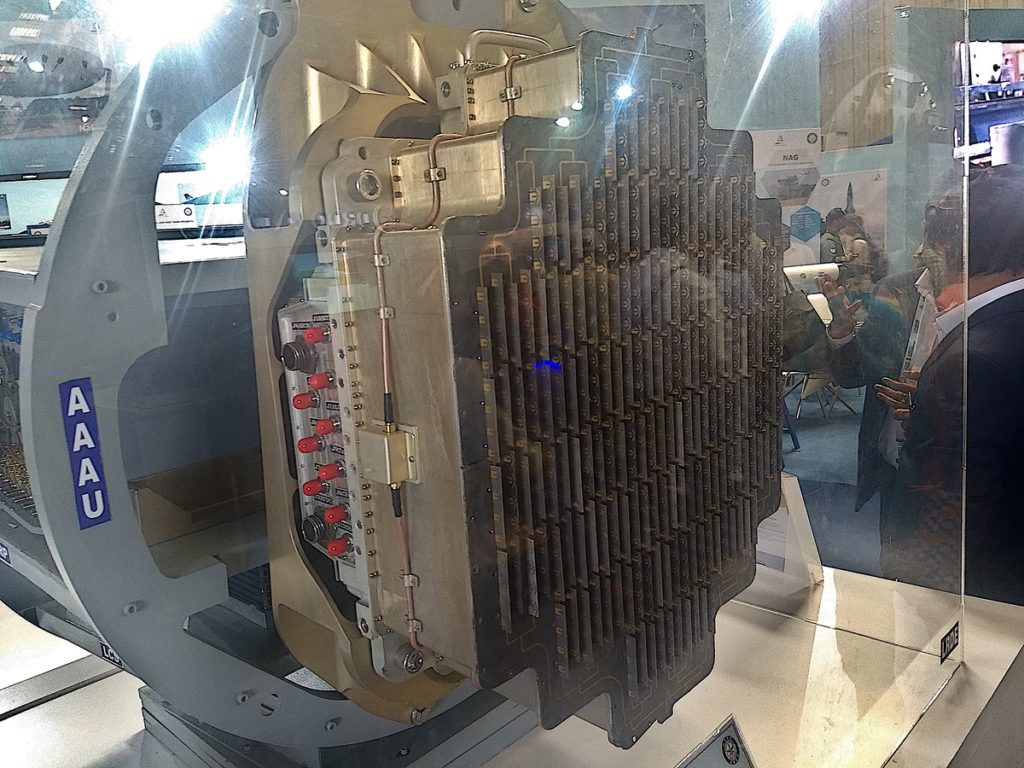
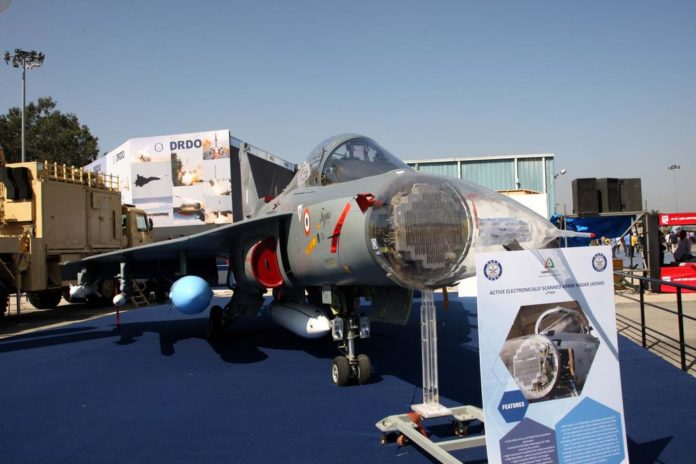
The licensing agreement is signed between LRDE and HAL to produce the Uttam Radar for LCA Tejas Mk1A, Tejas Mk2, AMCA, and TEDBF fighter jets. IAF also intends to equip the Su-30 Mki and MiG 29 UPG with this AESA Radar.
Read More: AMCA – India’s 5th Gen Fighter Jet






 Order Now on Amazon
Order Now on Amazon
