Nuclear weapons remain one of the most powerful deterrents in international security. Nations that possess nuclear weapons have developed delivery systems that launch warheads from land, air, and sea, forming what experts call a ‘nuclear triad’. India is one such country, uniquely positioned with a fully operational nuclear triad
A nuclear triad refers to a country’s ability to launch nuclear weapons from three platforms: land-based ballistic missiles, air-delivered nuclear bombs or missiles, and submarine-launched ballistic missiles.
As of now, only a few countries have developed and maintained a credible nuclear triad: the United States, Russia, China, India, and France. The United Kingdom is close, with its sea and air components fully operational.
The triad allows a country to launch a devastating counterstrike in response to a nuclear attack, even if an enemy disables one or two platforms.
Are Nuclear Missile Locations Public?
Most countries can track nuclear missile installations on land using satellite imagery and other intelligence methods. Radar systems can detect and track nuclear-capable fighter jets and bombers by following their flight paths and emissions. However, nuclear submarines especially ballistic missile submarines operate underwater stealthily, making them incredibly difficult to detect
India’s Land, Air and Sea Nuclear Arsenal
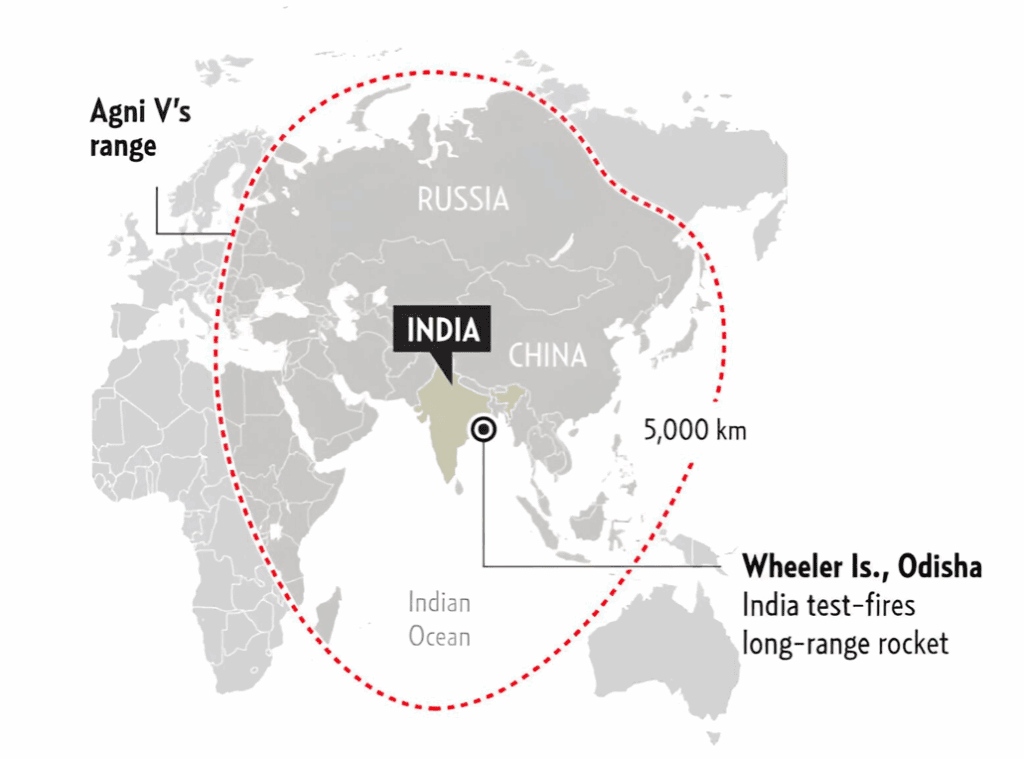
Agni Series – India’s land-based nuclear missile force includes missiles like the Agni series. For example, the Agni-V missile has an estimated range of around 5,000–5,500 kilometers, capable of reaching most parts of Asia, including China and parts of Europe. The Agni-IV and Agni-III have shorter ranges but are also potent.
In the air, India’s nuclear delivery is primarily through fighter jets such as the Dassault Rafale, Sukhoi su30, Mirage 2000 and the Jaguar, which can carry nuclear-capable air-to-surface missiles
On the sea front, India’s nuclear submarine program is spearheaded by the Arihant-class submarines launched ballistic missile. The primary nuclear-capable submarines in India’s arsenal are the INS Arihant and its sister ships, INS Arighat and INS Aridhaman. They also have codename like S73, S74 and S75 respectively
Who Holds Authority Over Nuclear Weapons?
In India, the ultimate authority to use nuclear weapons lies with the Nuclear Command Authority (NCA), which is chaired by the Prime Minister.
The NCA has two key components the Political Council, which authorizes the use of nuclear weapons, and the Executive Council, which assists in decision-making and execution. This structure ensures civilian control over nuclear weapons, with multiple checks to prevent unauthorized use.
Globally, command and control systems vary. The United States has a “sole authority” system where the President has exclusive control to launch nuclear weapons. Russia also vests authority in its president, with a highly centralized command. China’s nuclear weapons use authority lies with the Central Military Commission chaired by the General Secretary of the Communist Party.






 Order Now on Amazon
Order Now on Amazon
